What is a COIN porting agreement?
- by Qupra Wholesale B.V.
- in COIN transfer
- on August 12, 2021
When porting is done in COIN context, a porting agreement is created (version 8.7). Among other things, this agreement provides:
The recipient guarantees that he is authorized by the porter to: a. terminate the agreement between the porter and donor regarding the provision of a telecommunications service on behalf of the porter, and b. donor who is the holder of the Number to proceed with porting that Number. c. In concrete cases, explicitly mentioned in the Documents, this main rule may be deviated from.
Before the recipient with whom the porter wishes to enter into an agreement for the provision of public telecommunications services, submits a request for porting a Number to the donor, the latter must ensure that he has proof of his will showing that the recipient has the porter is authorized and which proof must meet the applicable criteria as established in the methods and procedure of authorization as defined in the documents.
The recipient who is under the obligation to receive an authorization as referred to in this Article 6 from the porter will, at the request of the donor referred to in Article 5, paragraph 1a, provide sufficient proof that the authorization has been issued in accordance with the criteria as defined in the documents. . The recipient’s obligation to provide sufficient evidence lapses 6 months after receipt of the relevant authorization.
The recipient who is under the obligation to receive an authorization as referred to in this Article 5 from the porter, will make every effort to ascertain the identity and, if relevant, the power of representation of the porter.
According to COIN, who requests porting?
The service provider + network provider make the request in COIN for a switch of telephone number or service.
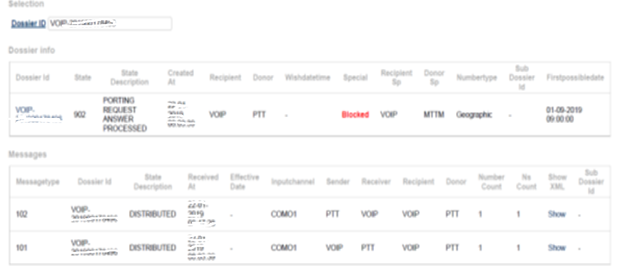
The service provider + network provider make the request in COIN for a switch of telephone number or service. From the transfer message from COIN below, an example screen shot of the member portal on COIN.nl, it can be concluded that in this example service provider RoutIT/KPN (using an SP code from RoutIT/KPN: VOIP) requests porting through RoutIT/KPN’s network code ( NO code: VOIP.)
This example from COIN shows that the service provider, with SP code from Routit/KPN BV: requests VOIP for porting.
RoutIT/KPN is therefore the party here, through its supplier PortingXS, which requests porting through its Service Provider Code (SP: VOIP) and Network Operator Code: VOIP. There is at Qupra CS. so no other party known than RoutiT/KPN that requests porting. RoutIT/KPN is both Service Provider and Network Provider in message traffic, and apparently fulfills this role for its reseller/partner, however, in accordance with Article 2.1 TW and the COIN regulations, a request must come from the Service Provider; in this case the partner of RoutIT. Because the Routit party is not registered in COIN, this is invisible to the other telecom providers with whom it is porting/switching.
Routit/KPN is the service provider & network provider requesting porting. COIN confirms this in its E-mail to Qupra that the list of members is online. This shows that code MTTM stands for Qupra and code VOIP for RoutIT/KPN BV. As the portal reports:
| Name | Operator Code | Sp Code | Email adress Helpdesk | Phone | Fax | Mobile | Manager Helpdesk | Active From |
| Routit/KPN B.V. | VOIP | VOIP | number-port@routit.nl | 088-4372629 | – | – | Jose van Velthuizen | 30-11-2007 |
Do you want to become a telecom reseller?
As a reseller partner, do you always want to comply with the regulations regarding porting and switching? Please contact rob@qupra.nl or leave your details here, we will send you an example of the data required for a valid expression of will and keep you informed of laws and regulations, so that you as a partner comply with the telecom law and ACM regulations. For a clear overview of all Qupra services, go to https://quprawholesale.com/services/.